Many times I get complaints from my clients that Wi-Fi is slow. They say we have tested from wired and we are getting X Mbps but once we test from wireless we are getting much slower speeds. The Access Point datasheet says these APs can support 1,733 Mbps but we are not getting such speeds! This series of posts aims to explain the factors that influence the speeds that we can get on Wi-Fi. In part 1, we will only give a high level overview of the involved entities.
GOING BACK TO BASICS OF WI-FI
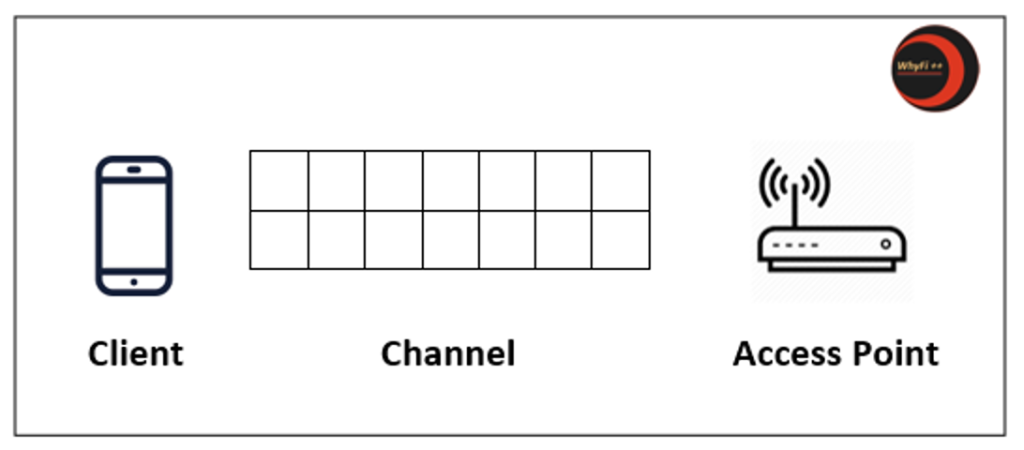
Let’s consider a communication from a client to an Access Point. There are three entities involved
- The client (acting as the transmitter)
- The access point (acting as the receiver)
- The “channel” (acting as the logical connection to transmit the message from the client to the access point)
Anything beyond the Access Point is part of the wired network. It will definitely play a huge role in the overall throughput but let’s first focus on the RF part. If you are interested to learn of what can possibly impact performance, check this extensive list from WLAN professionals.
Based on the above, any of the above 3 components can influence the overall throughout that can be achieved.
CLIENT’S IMPACT
Different clients have different wireless capabilities, this can definitely impact the wireless throughput. A mobile’s phone performance might be very different as compared to a laptop. This will be explained in details in Part 2.
CHANNEL’S IMPACT
The wireless channel will impact performance. Wireless, unlike wired, is a shared medium and devices will contend to transmit over Wi-Fi. Things like signal strength, noise, channel utilization, channel width, adjacent channel interference, co-channel interference..etc. can impact performance. This will be explained in details in Part 3. Note by the word channel, I don’t mean the channel number but I mean everything that happens on RF medium between the client and the Access Point.
The access point capabilities will impact the performance. The performance of an 802.11b/g access point be different from an 802.11ac or 802.11ax access point. This will be explained in details in Part 4.
Access Point’s Impact
Finally, in part 5, we will provide some recommendations on how to measure the performance. Is it really a Wi-Fi problem or is it something else? In the next part, we will start by focusing on the client.





One comment